to
{{errors.searchString}}
Select an eclipse from the list below.
| Date | Type | Duration | Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| {{eclipseDateString(eclipse)}} | {{eclipseType(eclipse)}} | {{eclipseMaxDuration(eclipse)}} | {{eclipse.continent}} |
{{filteredEclipses.length}} eclipses
{{eclipseTitle(selectedEclipse)}}
+
Log in or sign up to save your markers between visits.
Max Duration
{{eclipseMaxDuration(selectedEclipse)}}
Path Width
{{eclipsePathWidth(selectedEclipse)}}
Magnitude
{{selectedEclipse.magnitude}}
Local Circumstances at {{local.marker ? 'Marker' : 'Crosshairs'}}
Coordinates
Maximum
{{local.maxEclipse || ''}}
Duration
{{local.duration || ''}}
Magnitude
{{local.mag || ''}}
1st Contact
{{local.firstContact || ''}}
2nd Contact
{{local.secondContact || ''}}
3rd Contact
{{local.thirdContact || ''}}
Last Contact
{{local.lastContact || ''}}
Sunrise
{{local.sunrise || ''}}
Sunset
{{local.sunset || ''}}
City
{{local.marker.forecast.city.name}}
PROTECT YOUR EYES
The only time it is safe to view a solar eclipse without eye protection is during totality.
At all other times, look through safe solar viewing glasses (“eclipse glasses”) or
a safe handheld solar viewer.
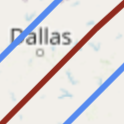 The red line is the centerline of the eclipse: the points along the eclipse path having
the longest duration of totality. The blue lines are the bounds of totality. You must be
within the blue bounds to see a total eclipse. For the best eclipse experience, you should
try to be as close to the centerline as possible.
The red line is the centerline of the eclipse: the points along the eclipse path having
the longest duration of totality. The blue lines are the bounds of totality. You must be
within the blue bounds to see a total eclipse. For the best eclipse experience, you should
try to be as close to the centerline as possible.
General
Drag the map around (use two fingers to drag). The crosshairs
at the center of the map show the "active" location. At the bottom-right you'll see a link with the time
and duration of totality at the active location (e.g. 6:57:52 GMT 4m04s).
You'll notice that the duration drops to zero otside the blue bands. You must be within the blue bands to see a total eclipse.
Tap the link to see additional details.
Markers and Weather Forecasts
Click the icon to drop a marker at the crosshairs.
You can add up to {{maxMarkerNum}} markers to the map and, if you're logged in, your markers will be
saved so you can see them the next time you visit. When you click on a marker you'll see
eclipse details at the marker's location and also a 5-day weather forecast for the location.
When the eclipse begins to fall within the 5-day forecast range, the app will start calculating
projected cloud cover at eclipse time and the color of the marker will change to
reflect this:

Eclipse not yet in forecast range.

Sparse cloud cover.

Moderate cloud cover.

Significant cloud cover.
Map Controls
Fly to the location having the greatest eclipse magnitude and duration of any point along the eclipse path.
Fly to a city, town or latitude/longitude coordinates.
Sets a map view to contain all of your markers at the maximum zoom level possible.
Add a draggable marker to the map. Log in or create an account to save your markers between visits.
Measure distances. When turned on, you can tap anywhere on the map to begin a line segment. Tap
at other points to add segments. Tap the end circle on the last segment a second time to complete
your path. Click the ruler icon again turn off measuring and erase your paths.
View eclipse details (time of eclipse, duration, etc.) at the selected location.
You can also do this by clicking a marker or the time and duration link under
the lower right corner of the map.
Solar Eclipse Glossary
Total
An eclipse where the apparent diameter of the Moon is large enough to completely cover the Sun's photosphere and reveal the solar corona.
Annular
An eclipse where the apparent diameter of the Moon is too small to completely cover the Sun. At mideclipse, the Sun appears as a bright ring around the Moon.
Hybrid
An eclipse that begins as an annular, becomes total for a brief time, and then reverts back to an annular before it ends. Rarely, a hybrid eclipse may begin as an annular and end as a total, or vice versa.
Partial
An eclipse where the Moon covers only a portion of the Sun. A partial eclipse precedes and follows totality or annularity, but a partial can also occur by itself. A partial solar eclipse is visible over a wider swath of Earth than is totality or annularity.
Maximum
The instant between 2nd and 3rd contact of a total solar eclipse, during which the Moon's disk completely covers the Sun's face.
Duration
The time between 2nd and 3rd contact during a total or annular solar eclipse.
Magnitude
The magnitude of the eclipse. Reflects the apparent size of the Moon relative to the solar disk. Will be greater than 1 for total eclipses and less than 1 for annular eclipses.
1st Contact
The moment when the Moon first touches the solar disk. The beginning of the partial phase of an eclipse
2nd Contact
The instant when the total or annular phase of an eclipse begins.
3rd Contact
The instant when the total or annular phase of a solar eclipse ends.
Last Contact
The instant when the Moon no longer covers any part of the solar disk. The conclusion of the partial phase of an eclipse.
